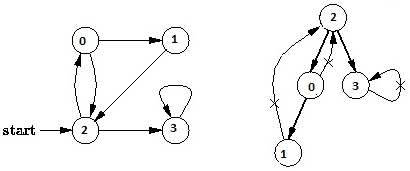
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
| 1 using System;
2 using System.Collections.Generic;
3
4 namespace GraphAlgorithmTesting
5 {
6 class Program
7 {
8 static void Main(string[] args)
9 {
10 Graph g = new Graph(4);
11 g.AddEdge(0, 1);
12 g.AddEdge(0, 2);
13 g.AddEdge(1, 2);
14 g.AddEdge(2, 0);
15 g.AddEdge(2, 3);
16 g.AddEdge(3, 3);
17
18 List<int> traversal = g.BFS(2);
19 foreach (var vertex in traversal)
20 {
21 Console.WriteLine(vertex);
22 }
23
24 Console.ReadKey();
25 }
26
27 class Edge
28 {
29 public Edge(int begin, int end)
30 {
31 this.Begin = begin;
32 this.End = end;
33 }
34
35 public int Begin { get; private set; }
36 public int End { get; private set; }
37 }
38
39 class Graph
40 {
41 private Dictionary<int, List<Edge>> _adjacentEdges
42 = new Dictionary<int, List<Edge>>();
43
44 public Graph(int vertexCount)
45 {
46 this.VertexCount = vertexCount;
47 }
48
49 public int VertexCount { get; private set; }
50
51 public void AddEdge(int begin, int end)
52 {
53 if (!_adjacentEdges.ContainsKey(begin))
54 {
55 var edges = new List<Edge>();
56 _adjacentEdges.Add(begin, edges);
57 }
58
59 _adjacentEdges[begin].Add(new Edge(begin, end));
60 }
61
62 public List<int> BFS(int start)
63 {
64 List<int> traversal = new List<int>();
65 int current = start;
66
67
68 bool[] visited = new bool[VertexCount];
69 for (int i = 0; i < VertexCount; i++)
70 {
71 visited[i] = false;
72 }
73
74
75 Queue<int> queue = new Queue<int>();
76
77
78 visited[current] = true;
79 queue.Enqueue(current);
80
81 while (queue.Count > 0)
82 {
83 current = queue.Dequeue();
84
85
86 traversal.Add(current);
87
88
89
90
91 if (_adjacentEdges.ContainsKey(current))
92 {
93 foreach (var edge in _adjacentEdges[current])
94 {
95 if (!visited[edge.End])
96 {
97 visited[edge.End] = true;
98 queue.Enqueue(edge.End);
99 }
100 }
101 }
102 }
103
104 return traversal;
105 }
106 }
107 }
108 }
|