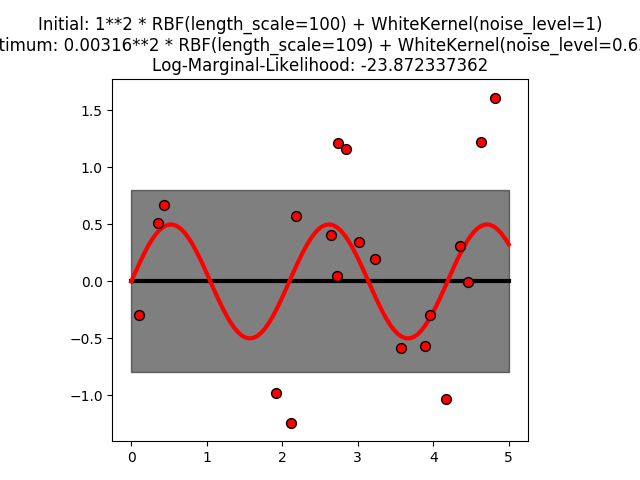
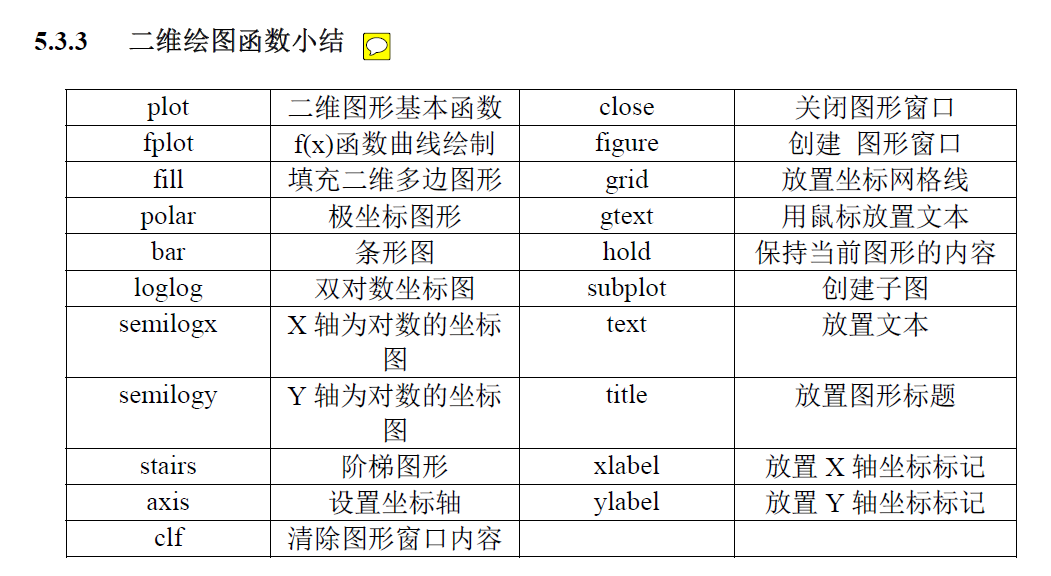
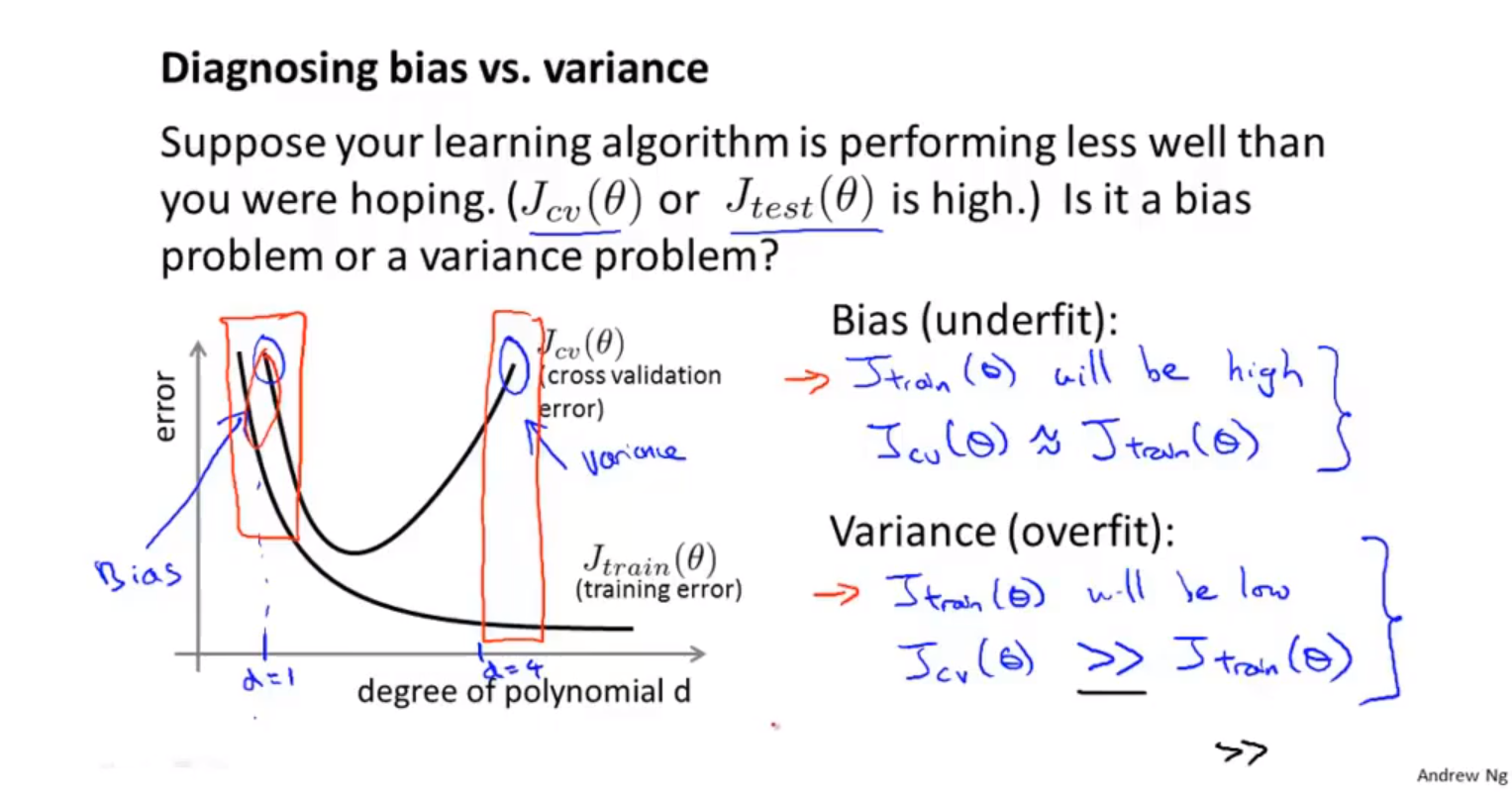
3D与动画 基本方法 本章知识点归纳如下:
创建3D图:ax = Axes3D(fig)
画出3D图:ax.plot_surface()
投影:ax.contourf()
动画:animation.FuncAnimation()
3D作图 首先在进行 3D Plot 时除了导入 matplotlib ,还要额外添加一个模块,即 Axes 3D 3D 坐标轴显示,并且之后要先定义一个图像窗口,在窗口上添加3D坐标轴,显示成下图:
1 2 3 4 5 6 import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3Dfig = plt.figure() ax = Axes3D(fig)
接下来给进 X 和 Y 值,并将 X 和 Y 编织成栅格。每一个(X, Y)点对应的高度值我们用下面这个函数来计算:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 X = np.arange(-4 , 4 , 0.25 ) Y = np.arange(-4 , 4 , 0.25 ) X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y) R = np.sqrt(X ** 2 + Y ** 2 ) Z = np.sin(R)
做出一个三维曲面,并将一个 colormap rainbow 填充颜色,之后将三维图像投影到 XY 平面上做一个等高线图。其中,rstride 和 cstride 分别代表 row 和 column 的跨度。跨度越小,图形上的网格越密集,实际画出的 plot 3D 图像会如下图所示:
1 2 3 4 fig = plt.figure() ax = Axes3D(fig) ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1 , cstride=1 , cmap=plt.get_cmap('rainbow' )) <mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.art3d.Poly3DCollection at 0x7fcec6cf8320 >
投影 有时候我们在观察3D图形时,可能需要图形映射到平面中来观察。还记得之前学习过的等高线图吗,它可以帮助我们对3D图像进行投影。下面代码为添加 XY 平面的等高线,如果 zdir 选择了x,那么效果将会是对于 XZ 平面的投影,而调整offset可以调整投影出现的位置,整体效果如下:
1 2 3 4 5 fig = plt.figure() ax = Axes3D(fig) ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1 , cstride=1 , cmap=plt.get_cmap('rainbow' )) ax.contourf(X, Y, Z, zdir='z' , offset=-1 , cmap=plt.get_cmap('rainbow' )) <matplotlib.contour.QuadContourSet at 0x7fcec4b6aba8 >
如果 zdir 选择了x,那么效果将会是对于 XZ 平面的投影,效果如下:
1 2 3 4 5 fig = plt.figure() ax = Axes3D(fig) ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1 , cstride=1 , cmap=plt.get_cmap('rainbow' )) ax.contourf(X, Y, Z, zdir='x' , offset=-4 , cmap=plt.get_cmap('rainbow' )) <matplotlib.contour.QuadContourSet at 0x7fcec4919a90 >
Animation 动画 最后,matplotlib还为我们提供了动画的接口。我们将使用其中一种方式 function animation 来为大家讲解,具体可参考matplotlib animation api。下面,我们就开始吧!
导入动画库并定义方程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from matplotlib import animation import numpy as np fig, ax = plt.subplots() x = np.arange(0, 2*np.pi, 0.01) line, = ax.plot(x, np.sin(x))
构造动画函数与帧函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 def animate(i): line.set_ydata(np.sin(x + i/10.0)) return line, def init(): line.set_ydata(np.sin(x)) return line,
参数设置:
fig 进行动画绘制的figure
func 自定义动画函数,即传入刚定义的函数animate
frames 动画长度,一次循环包含的帧数
init_func 自定义开始帧,即传入刚定义的函数init
interval 更新频率,以ms计
lit 选择更新所有点,还是仅更新产生变化的点。应选择True,但mac用户请选择False,否则无法显示动画
(因为平台的不兼容问题,请klab暂时无法进行动画的演示,请大家在自己的电脑上尝试进行动画作图吧~)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 fig, ax = plt.subplots() line, = ax.plot(x, np.sin(x)) ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig=fig, func=animate, frames=100 , init_func=init, interval=20 , blit=True ) plt.show()
当然,你也可以将动画以mp4格式保存下来,但首先要保证你已经安装了ffmpeg 或者mencoder
1 ani.save('basic_animation.mp4', fps=30, extra_args=['-vcodec', 'libx264'])
练一练 请大家根据之前所学的3D图画法画出3D数据 z = (x + y)^2, 并利用等高线图对其进行投影。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 #参考答案: X = np.arange(-4, 4, 0.25) Y = np.arange(-4, 4, 0.25) X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y) Z = (X + Y)**2 fig = plt.figure() ax = Axes3D(fig) ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=plt.get_cmap('rainbow')) ax.contourf(X, Y, Z, zdir='x', offset=-4, cmap=plt.get_cmap('rainbow')) <matplotlib.contour.QuadContourSet at 0x7fcec4416400>