lambda表达式
1 简介
对象分类
对象的分类
- 基础类型的对象
- 复合类型的对象
- 类类型的对象
- 函数对象
可调用对象
可调用对象是可以使用函数调用运算符()的对象。
- 函数
- 函数指针
- 重载了函数调用运算符的类
- lambda表达式
2 使用
Lambda表达式定义
- 形式。仅仅是形式上不同的函数。capture list捕获列表是外部的局部变量的列表,捕获后可以在函数内部使用。
1
| [capture list](parameter list) -> return type {function body}
|
1
2
3
| auto l=[]{
cout<<"hello world"<<endl;
}
|
1
| []{ cout<<"helloworld"<<endl;}();
|
1
| auto l = [](int a,int b){cout<<a+b<<endl;};
|
1
| auto l = [](int m,int n)->int{cout<<m+n<<endl;return m+n;};
|
lambda表达式的调用
1
2
| auto f = []{return 42;};
cout<<f()<<endl;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| //使用find_if和lambda表达式
vector<string> words={"abc","a","bc","feiao"};
int sz =4;
auto wc = find_if(words.begin(),words.end(),
[sz](const string &a){
return a.size()>=sz;
}
);
cout<<(*wc)<<endl;
return 0;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| // for_each给每一个元素的操作
int sz2 = 3;
for_each(words.begin(),words.end(),
[sz2](const string&a){
if(a.size()>=sz2){
cout<<a<<endl;
}
}
);
|
捕获列表
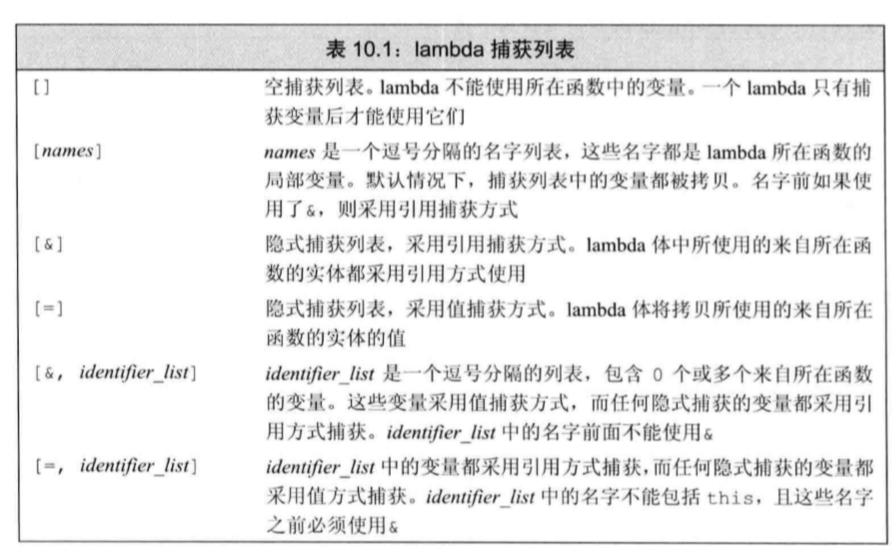
1
2
3
4
| int a = 1;
auto f = [&a]{
return a;
};
|
返回类型
可以指定返回值的类型。
- 单个返回语句可以推断返回类型,不需要指定返回值类型
- 多个返回语句无法推断。需要指定返回类型。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| transoform(vi.begin(),vi.end(),vi.begin(),
[](int i)->int{
if(i<0)return -i;
else return i;
}
);
|
3 bind 参数绑定
lambda 表达式通常只在一个地方使用的简单操作。如果需要在多个地方使用相同的操作,通常定义一个函数,而不是多次编写相同的lambda表达式。
bind函数适配器,接受一个函数对象,生成一个行的可调用的对象。
1
2
| auto newCallable = bind(callable,arg_list);
auto g = bind(f,a,b,_2,c,_1);
|











