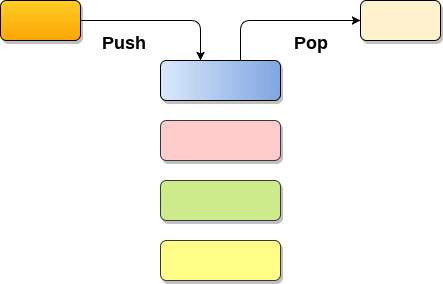
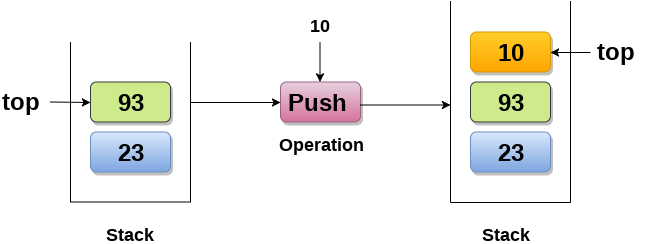
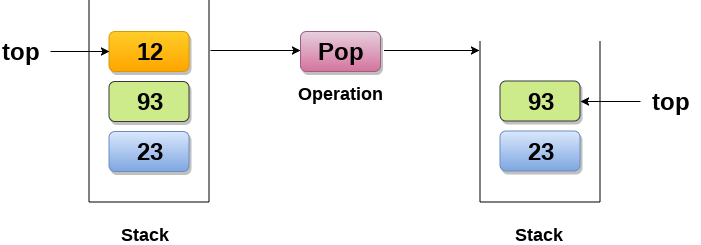
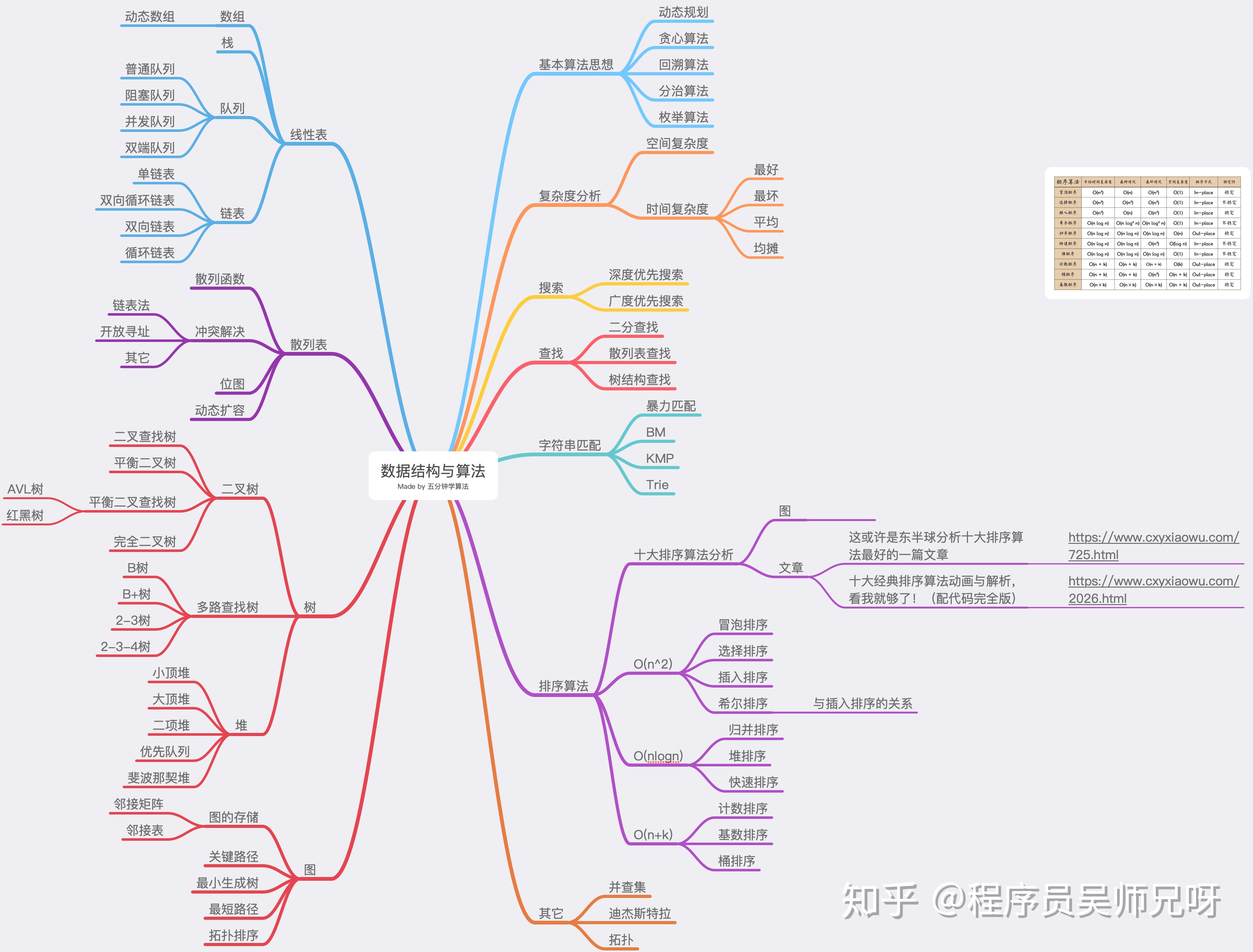
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
| #include <stdio.h>
int stack[100], i, j, choice = 0, n, top = -1;
void push();
void pop();
void show();
void main()
{
printf("Enter the number of elements in the stack ");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("*********Stack operations using array*********");
printf("----------------------------------------------\n");
while (choice != 4)
{
printf("Chose one from the below options...\n");
printf("1.Push\n2.Pop\n3.Show\n4.Exit");
printf("Enter your choice \n");
scanf("%d", &choice);
switch (choice)
{
case 1:
{
push();
break;
}
case 2:
{
pop();
break;
}
case 3:
{
show();
break;
}
case 4:
{
printf("Exiting....");
break;
}
default:
{
printf("Please Enter valid choice ");
}
};
}
}
void push()
{
int val;
if (top == n)
printf("Overflow");
else
{
printf("Enter the value?");
scanf("%d", &val);
top = top + 1;
stack[top] = val;
}
}
void pop()
{
if (top == -1)
printf("Underflow");
else
top = top - 1;
}
void show()
{
for (i = top;i >= 0;i--)
{
printf("%d\n", stack[i]);
}
if (top == -1)
{
printf("Stack is empty");
}
}
|