观察者模式
别名
- Dependency
- Publish-Subscribe
观察者模式好牛啊,在不同的代码层次有这不同的名称但是大同小异。
- 在java代码层就是观察着模式
- 在socket网络编程、IO编程中(netty、springWebFlux、sofarpc)就是Reactor模式
- 在操作系统中就是IO多路复用的一种策略
- 在UI框架中就是Listener,事件监听机制和响应机制
- 在Spring框架中也有事件监听模型。
- 在web网站开发中,被称为响应式编程。
服务发现机制。以下并不是观察者模式的范畴,是一种更加宏观的机制,可能使用了观察者模式去发现。
- javaSPI。服务提供者接口
- 在微服务中就是注册中心的发布订阅过程。发布者订阅者、提供者消费者。
- 在消息中间件中就是发布订阅模式。
https://juejin.cn/post/6993999863159455752
意图
定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,当一个对象的状态发生改变时,所有依赖于它的对象都得到通知并被自动更新。
结构
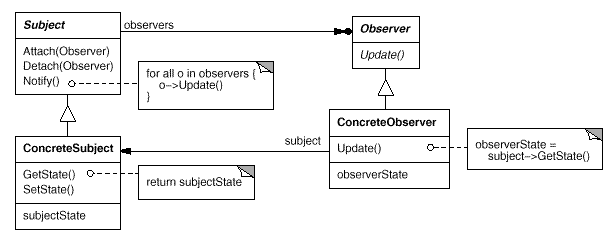
参与者
Subject
Observer
- 为那些在 Subject 发生改变时需要获得通知的对象定义一个 Update 接口。
ConcreteSubject
ConcreteObserver
维护一个指向 ConcreteSubject 对象的引用。
存储有关状态,这些状态应该与 ConcreteSubject 的状态保持一致。
实现 Observer 的更新接口以使自身状态与 ConcreteSubject 状态保持一致。
适用性
在以下情况下可以使用 Observer 模式:
当一个抽象模型有两个方面,其中一个方面依赖于另一个方面。将这二者封装在独立的对象中以使它们可以各自独立地改变和复用。
当对一个对象的改变需要同时改变其他对象,而不知道具体有多少对象有待改变。
当一个对象必须通知其他对象,而它又不能假定其他对象时谁。
效果
相关模式
- 可以使用 Mediator 模式封装复杂的更新语义,充当 Subject 与 Observer
之间的中介者。
Implementation
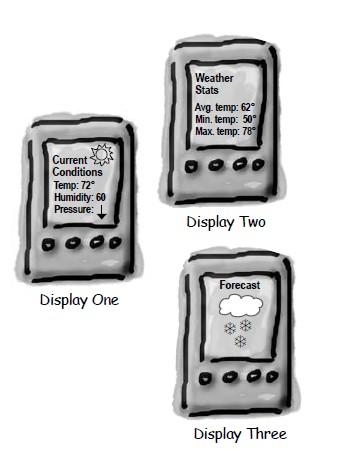
天气数据布告板会在天气信息发生改变时更新其内容,布告板有多个,并且在将来会继续增加。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public interface Subject {
void registerObserver(Observer o);
void removeObserver(Observer o);
void notifyObserver();
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| public class WeatherData implements Subject {
private List<Observer> observers;
private float temperature;
private float humidity;
private float pressure;
public WeatherData() {
observers = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void setMeasurements(float temperature, float humidity, float pressure) {
this.temperature = temperature;
this.humidity = humidity;
this.pressure = pressure;
notifyObserver();
}
@Override
public void registerObserver(Observer o) {
observers.add(o);
}
@Override
public void removeObserver(Observer o) {
int i = observers.indexOf(o);
if (i >= 0) {
observers.remove(i);
}
}
@Override
public void notifyObserver() {
for (Observer o : observers) {
o.update(temperature, humidity, pressure);
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
| public interface Observer {
void update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class StatisticsDisplay implements Observer {
public StatisticsDisplay(Subject weatherData) {
weatherData.registerObserver(this);
}
@Override
public void update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure) {
System.out.println("StatisticsDisplay.update: " + temp + " " + humidity + " " + pressure);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class CurrentConditionsDisplay implements Observer {
public CurrentConditionsDisplay(Subject weatherData) {
weatherData.registerObserver(this);
}
@Override
public void update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure) {
System.out.println("CurrentConditionsDisplay.update: " + temp + " " + humidity + " " + pressure);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public class WeatherStation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WeatherData weatherData = new WeatherData();
CurrentConditionsDisplay currentConditionsDisplay = new CurrentConditionsDisplay(weatherData);
StatisticsDisplay statisticsDisplay = new StatisticsDisplay(weatherData);
weatherData.setMeasurements(0, 0, 0);
weatherData.setMeasurements(1, 1, 1);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
| CurrentConditionsDisplay.update: 0.0 0.0 0.0
StatisticsDisplay.update: 0.0 0.0 0.0
CurrentConditionsDisplay.update: 1.0 1.0 1.0
StatisticsDisplay.update: 1.0 1.0 1.0
|
JDK