3.6 享元
享元模式
意图
运用共享技术有效地支持大量细粒度的对象。
Use sharing to support large numbers of fine-grained objects efficiently.
结构
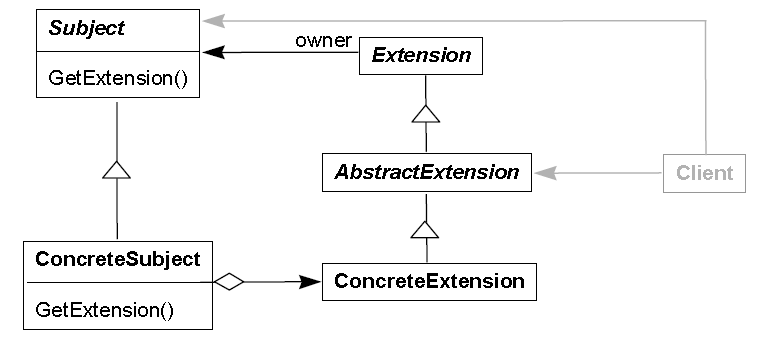
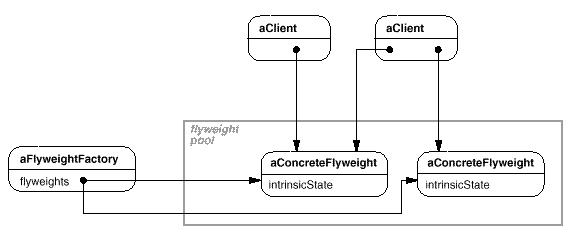
下面的对象图说明了如何共享 Flyweight:
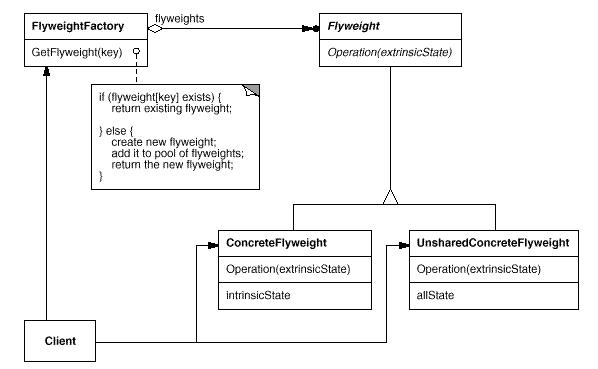
参与者
Flyweight
- 描述一个接口,通过这个接口 Flyweight 可以接受并作用于外部状态。
ConcreteFlyweight
- 实现 Flyweight
接口,并为内部状态增加存储空间。该对象必须是可共享的。它所存储的状态必须是内部的,即必须独立于对象的场景。
UnsharedConcreteFlyweight
- 并非所有的 Flyweight 子类都需要被共享。Flyweight
接口使共享成为可能,但它并不强制共享。
FlyweightFactory
创建并管理 Flyweight 对象。
确保合理地共享 Flyweight。
Client
维持一个对 Flyweight 的引用。
计算或存储 Flyweight 的外部状态。
适用性
Flyweight 模式的有效性很大程度上取决于如何使用它以及在何处使用它。
当以下情况成立时可以使用 Flyweight 模式:
一个应用程序使用了大量的对象。
完全由于使用大量对象,造成很大的存储开销。
对象的大多数状态都可变为外部状态。
如果删除对象的外部状态,那么可以用相对较少的共享对象取代很多组对象。
应用程序不依赖于对象标识。
效果
- 存储空间上的节省抵消了传输、查找和计算外部状态时的开销。节约量随着共享状态的增多而增大。
相关模式
Flyweight 模式通常和 Composite
模式结合起来,用共享叶节点的又向无环图实现一个逻辑上的层次结构。通常,最好用 Flyweight 实现 State 和 Strategy 对象。
Implementation
1 | public interface Flyweight { |
1 | public class ConcreteFlyweight implements Flyweight { |
1 | public class FlyweightFactory { |
1 | public class Client { |
1 | Object address: 1163157884 |
JDK
Java 利用缓存来加速大量小对象的访问时间。
- java.lang.Integer#valueOf(int)
- java.lang.Boolean#valueOf(boolean)
- java.lang.Byte#valueOf(byte)
- java.lang.Character#valueOf(char)
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来源 Estom的博客!