4 重新组织数据 1 Self Encapsulate Field(自封装字段) 直接访问一个字段,后面如果与该字段的耦合关系逐渐变得笨拙时,可以使用Self Encapsulate Field手法进行重构,为这个字段建立取值/设值函数,并且只以这些函数来访问字段。
重构示例10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 // 重构前 class Range { public: bool Includes(int arg) { return arg >= m_low && arg <= m_high; } private: int m_low; int m_high; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 // 重构后 class Range { public: bool Includes(int arg) { return arg >= GetLow() && arg <= GetHigh(); } private: int GetLow() { return m_low; } int GetHigh() { return m_high; } private: int m_low; int m_high; }
应该更多的赋予对象业务行为函数而不是过多的使用getter/setter函数,否则对象就会变成领域驱动设计里面所提到的贫血模型。
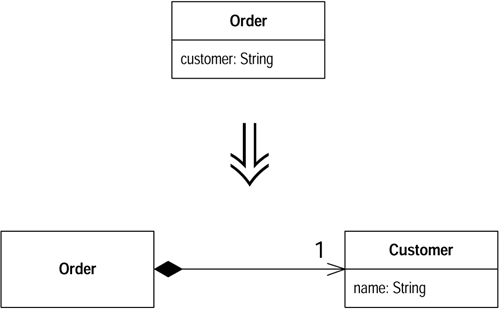
2 Replace Data Value with Object(以对象取代数据值) 软件开发初期,你往往会以简单的基本类型来表示某一概念,随着开发的迭代,这些概念不再是简单的基本类型就能表示的,这时就需要使用Replace Data Value with Object进行重构,封装一个新的对象来取代原有的基本类型数据值。比如重构示例8中,刚开始使用一个字符串来表示“电话号码”的概念,但随后就会发现,电话号码需要“格式化”、“抽取区号”之类的特殊行为,这些就需要将“电话号码”封装成一个对象了。
更好的方法是在设计阶段对通用语言进行领域建模,并赋予对象业务行为函数,这样可以使复杂的系统更加清晰。
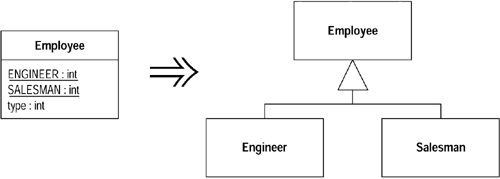
3 Replace Type Code with Subclasses(以子类取代类型码) 如果一个类中有一个不可变的类型码,而且它会影响到类的行为,这时就可以以子类来取代这个类型码。一般来说,这种情况的标志就是出现switch或if/else结构,它们检查类型码的值,并根据不同的值执行不同的动作。
Replace Type Code with Subclasses的好处在于,它把“对不同行为的了解”从类用户转移到了类自身。如果需要加入新的行为变化,只需添加一个子类即可。如果没有多态机制,就必须找到所有的条件表达式,并逐一修改它们。
重构示例11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Employee {public: Employee(int type) : m_type(type) {} int GetType () { return m_type; } public: static constexpr int ENGINEER = 0 ; static constexpr int SALESMAN = 1 ; static constexpr int MANAGER = 2 ; private: int m_type; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Employee {public: static Employee* Create (int type) { switch (type) { case ENGINEER: return new Engineer; case SALESMAN: return new Salesman; case MANAGER: return new Manager; default : return nullptr; } } virtual int GetType () = 0 ; private: Employee() = default ; public: static constexpr int ENGINEER = 0 ; static constexpr int SALESMAN = 1 ; static constexpr int MANAGER = 2 ; } class Engineer :public: int GetType () override { return Employee::ENGINEER; } }
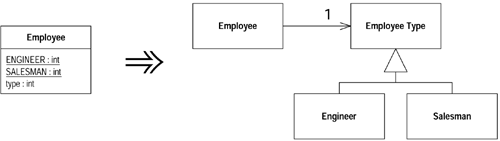
4 Replace Type Code with State/Strategy(以State/Strategy取代类型码) 如果一个类中有一个不可变的类型码,而且它会影响到类的行为,但是无法通过继承手法消除它时,就可以使用Replace Type Code with State/Strategy进行重构。如果是通过重构来简化一个算法,则Strategy模式比较合适;如果是打算搬移与状态相关的数据,而且把新建对象视为一种变迁状态,则State状态比较合适。
重构示例12 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 // 重构前 class Employee { public: Employee(int type) : m_type(type) {} int GetType() { return m_type; } int PayAmount() { switch (m_type) { case ENGINEER: return m_monthlySalary; case SALESMAN: return m_monthlySalary + m_commission; case MANAGER: return m_monthlySalary + m_bonus; default: return -1; } } public: static constexpr int ENGINEER = 0; static constexpr int SALESMAN = 1; static constexpr int MANAGER = 2; private: int m_type; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 class Employee {public: Employee(int type) : m_type(EmployeeType::ValueOf(type)) {} int GetType () { return m_type->GetTypeCode(); } int PayAmount () { switch (GetType()) { case EmployeeType::ENGINEER: return m_monthlySalary; case EmployeeType::SALESMAN: return m_monthlySalary + m_commission; case EmployeeType::MANAGER: return m_monthlySalary + m_bonus; default : return -1 ; } } private: EmployeeType* m_type; } class EmployeeType {public: static EmployeeType* ValueOf (int code) { switch (code) { case ENGINEER: return new Engineer; case SALESMAN: return new Salesman; case MANAGER: return new Manager; default : return nullptr; } } virtual int GetTypeCode () = 0 ; public: static constexpr int ENGINEER = 0 ; static constexpr int SALESMAN = 1 ; static constexpr int MANAGER = 2 ; } class Engineer :public: int GetTypeCode () override { return EmployeeType::ENGINEER; } }