4 TLS密钥协商
握手协议主要包括:密钥协商机制和密钥交换算法。基本的密钥协商机制是一样的,只是在不同的步骤交换的内容不一样。
握手是为了协商出一个client和server端都认可的一个对称秘钥,典型的秘钥协商算法有两种,RSA和ECDH,简明介绍下这两种算法会让你对这个过程更加清晰。
0 TLS1.1
协议构成
1 | enum { |
密钥交换算法
1 | Key Exchange Algorithm Certificate Key Type |
1 TLS1.2密钥协商机制
协议构成
- This protocol is used to negotiate the secure attributes of a session.
1 | enum { |
FULL Handshake密钥协商机制
- TLS1.2,它通过KeyExchange进行密钥协商,即ServerKeyExchange和ClientKeyExchange,那么密钥交换本身就需要一个交互来回,所以总共有四次握手交互。
1 | Client Server |
Session ID Handshake密钥协商机制
- TLS1.2 通过会话重建来加速完成密钥协商过程。
- 如果找到匹配项,并且服务器愿意重新建立指定会话状态下的连接,它将发送一个具有相同会话 ID 值的 ServerHello。此时,双方客户端和服务器必须发送更改密码规范消息并继续直接到完成的消息。一旦重新建立完成,客户端和服务器可以开始交换应用程序层数据。(请参见下面的流程图。)如果会话 ID 不匹配,服务器生成一个新的会话 ID, TLS 客户端和服务器执行完整的握手。
1 | Client Server |
key-exchange-algorithm密钥交换算法
1 | Key Exchange Alg. Certificate Key Type |
RSA key-exchange-algorithm密钥交换算法
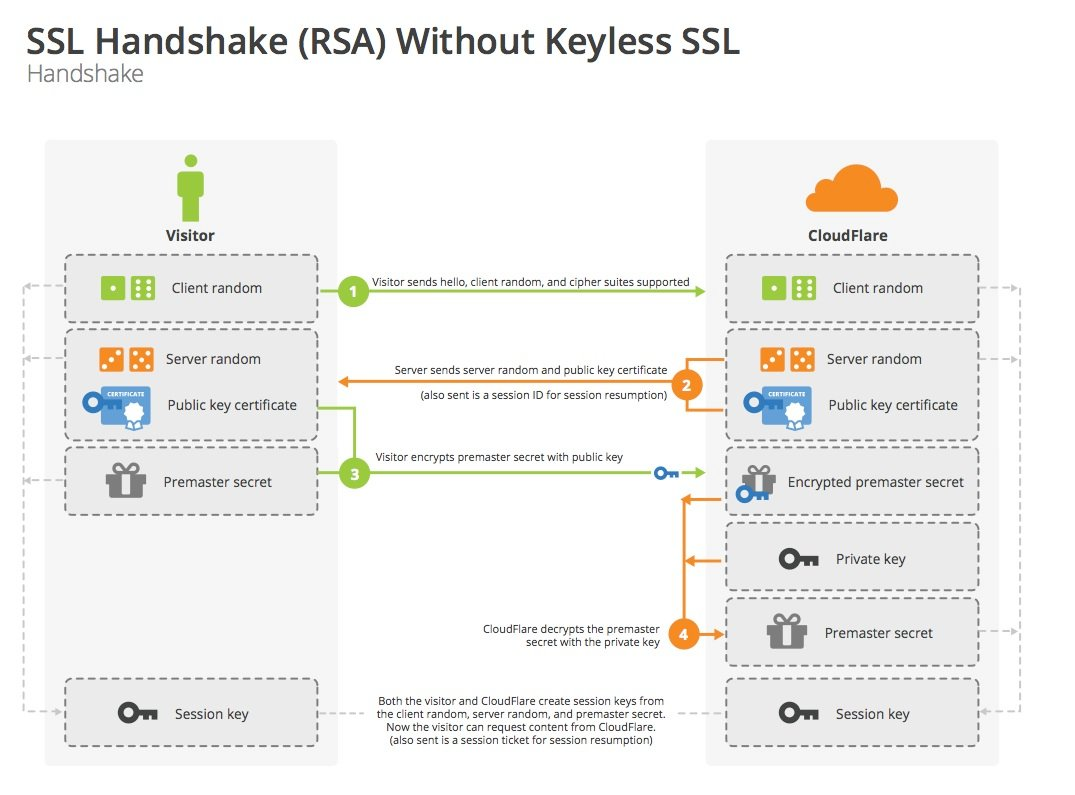
RSA 秘钥交换
- client 发起请求(Client Hello)
- server 回复 certificate
- client使用证书中的公钥,加密预主秘钥,发给 server(Client Key Exchange)
- server 提取出 预主秘钥,计算主秘钥,然后发送对称秘钥加密的finished。
- client 计算主秘钥,验证 finished,验证成功后,就可以发送Application Data了。
缺点:RSA秘钥交换不是前向安全算法(证书对应私钥泄漏后,之前抓包的报文都能被解密)。所以在 TLS 1.3中 RSA 已经废弃了。
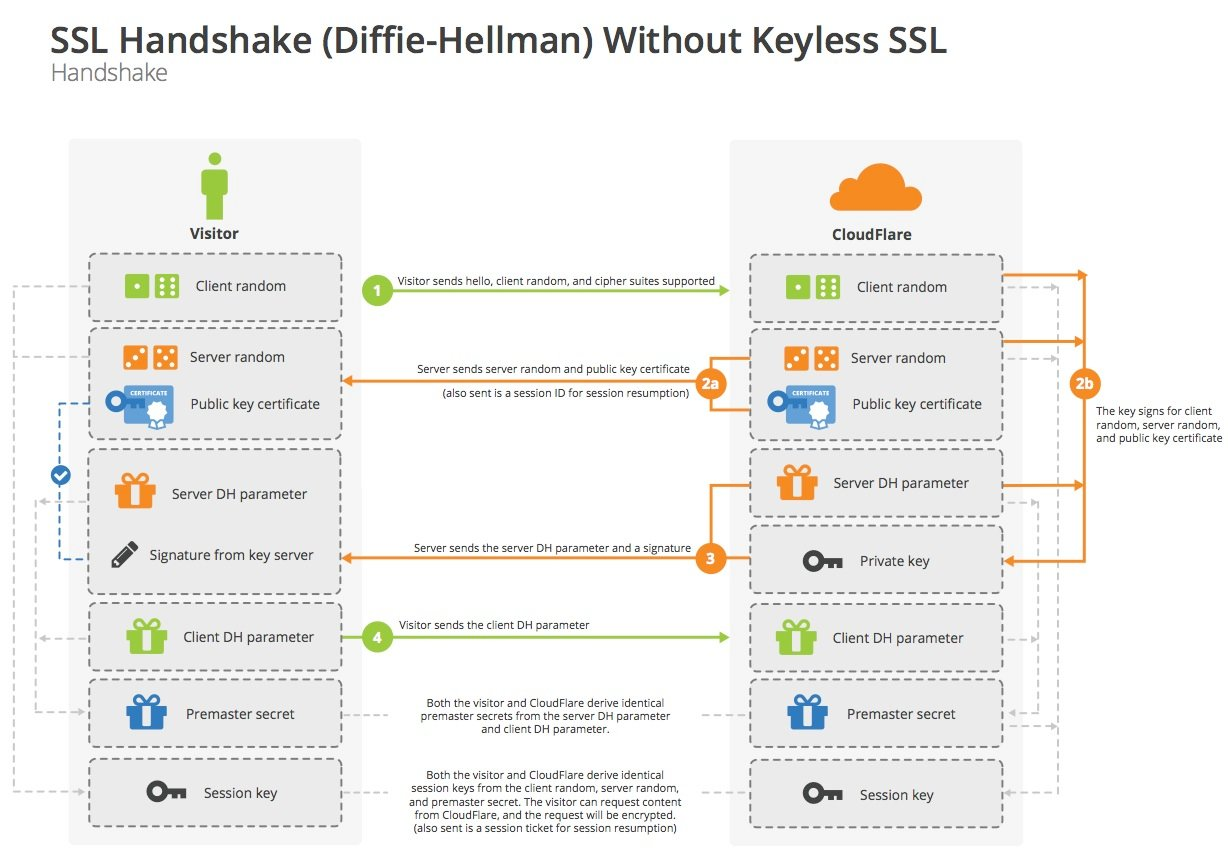
DH key-exchange-algorithm密钥交换算法
2 TLS1.3
协议构成
- The handshake protocol is used to negotiate the security parameters of a connection.
1 | enum { |
密钥协商机制+密钥交换算法
Full Handshake
(EC)DHE (Diffie-Hellman over either finite fields or elliptic
curves)PSK-only
PSK with (EC)DHE
0-RTT Handshake
FULL Handshake密钥协商机制
- TLS1.3,通过ClientHello和ServerHello的扩展进行密钥交换,那么就省去了1.2版本中KeyExchange的过程,也就省去了一次握手。
1 | Figure 1 below shows the basic full TLS handshake: |
- client 发送请求(Client Hello),extension携带支持的椭圆曲线类型。且对每个自己支持的椭圆曲线类型计算公钥(POINT)。公钥放在extension中的keyshare中。
- 支持的加密套件(该作用和之前一样)。
- supproted_versions 拓展。包含自己支持的TLS协议版本号。(之前协议没有)
- supproted_groups 拓展,表示自己支持的椭圆曲线类型。
- key_share拓展。包含supprot_groups中各椭圆曲线对应的public key。(当然可以发送空的,然后server会回复hello request,其中会包含server的key_share,可以用来探测,这里不讨论)。key_share中的椭圆曲线类型必须出现在supproted_groups中。(之前协议没有)
- server 回复 Server Hello和certificate等;server选择的椭圆曲线参数,然后乘以椭圆曲线的base point得到公钥(POINT)。然后提取Client Hello中的key_share拓展中对应的公钥,计算主秘钥。公钥(POINT)不再和之前的以协议一样放在Server Key Exchange中,而是放在Server Hello的key_share拓展中。client收到server的公钥(POINT)后计算主秘钥。
- (1):supproted_versions 拓展。包含自己从client的supproted_versions中选择的TLS协议版本号。(之前协议没有)
- (2):key_share拓展。包含自己选中的椭圆曲线,以及自己计算出来的公钥。(之前协议没有)
- server 发送Change Cipher Spec。(允许不发送)
- server发送Encrypted Extension。(加密的)ServerHello之后必须立刻发送Encrypted Extension。这是第一个被加密的数据数据。显然,放在这里的拓展,是和秘钥协商没关系的拓展。(之前协议没有)
- server发送Certificate(加密的)。这个报文和之前的协议没有太大区别,,在证书链中的每个证书后面,都有一个extension。(双向认证时也会有区别,有机会再说)。这个extension目前只能是OCSP Status extension和SignedCertificateTimestamps。
- server发送Certificate Verify(加密的)这个报文并不陌生,但是以前只出现在双向认证(客户端认证)中,以前Certificate Verify生成的逻辑是将当前所有的握手报文解析解析签名(简单的md+非对称加密)。
- server回复Finished(加密的)这个报文的目的和之前协议一样,检验握手报文的完整性。但是计算方法有变化。
DHE share Handshake
- If the client has not provided a sufficient “key_share” extension(e.g., it includes only DHE or ECDHE groups)
1 |
|
- client 发送请求(Client Hello),extension携带支持的椭圆曲线类型。
- server 回复 Server Hello和certificate等;server选择的椭圆曲线参数,然后 生成私钥(BIGNUM),乘以椭圆曲线的base point得到公钥(POINT),顺便签个名表示自己拥有证书,然后将报文发给client,报文就是Server Key Exchange,其包含了server选择的椭圆曲线参数、自己根据这个参数计算的公钥、自己用证书的私钥对当前报文的签名。
- client 收到 Server Key Exchange,获得椭圆曲线参数,生成私钥(BIGNUM)后计算公钥(POINT),然后把公钥发出去Client Key Exchange。client使用自己的私钥(BIGNUM)和server的公钥(POINT)计算出主秘钥。
- server 收到 client的公钥(POINT),使用自己的私钥(BIGNUM),计算主秘钥。两端主秘钥是一致。
PSK Handshake
- Resumption and Pre-Shared Key (PSK)
- 由于服务器通过 PSK 进行身份验证,因此它不会发送证书或 CertificateVerify 消息。
- 当客户提供通过 PSK 恢复,它还应该提供“key_share”扩展名到服务器允许服务器拒绝恢复,而是使用正常的full handshake过程。
- 服务器响应一个“pre_shared_key”扩展来协商使用 PSK 密钥。可以使用“key_share”响应扩展做(EC)DHE密钥建立。
1 | Client Server |
0-RTT Handshake
- TLS1.3 0-RTT模式密钥交换。以某些安全属性为代价。当client和server共享一个预共享密钥PSK(从外部获得或通过一个以前的握手获得)时,TLS 1.3允许client在第一个发送出去的消息的early data中携带数据,client使用这个PSK来认证server并加密early data。即在握手之前就有了PSK时,在第一次发送ClientHello时就可以发送加密数据,达到0-RTT数据传输的目的。
- This data is not forward secret, as it is encrypted solely under keys derived using the offered PSK.
1 | Client Server |
3 椭圆曲线原理
- ECDH的秘钥协商过程,首先EC的意思是椭圆曲线,这个EC提供了一个很厉害的性质,你在曲线上找一个点P,给定一个整数K,求解Q=KP很容易,给定一个点P,Q,知道Q =KP,求K却是个难题。
- 在这个背景下,给定一个大家都知道的大数G,client在每次需要和server协商秘钥时,生成一段随机数a,然后发送A=a*G给server。
- server收到这段消息(a*G)后,生成一段随机数b,然后发送B=b*G给client。
- server端计算(a*G)*b作为对称秘钥,client端收到后b*G后计算a*(G*b),因为(a*G)*b = a*(G*b),所以对称秘钥就是a*G*b啦。
- 攻击者只能截获A=a*G和B=b*G,由于椭圆曲线难题,知道A和G是很难计算a和b的,也就无法计算aGb了
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来源 Estom的博客!









