1 创建项目
1.1. maven设置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| <mirrors>
<mirror>
<id>nexus-aliyun</id>
<mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf>
<name>Nexus aliyun</name>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public</url>
</mirror>
</mirrors>
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>jdk-1.8</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
<jdk>1.8</jdk>
</activation>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8</maven.compiler.compilerVersion>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
|
1.2. 创建maven工程
1.3. 引入依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
1.4. 创建主程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class,args);
}
}
|
1.5. 编写业务逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String handle01(){
return "Hello, Spring Boot 2!";
}
}
|
1.6. 测试
直接运行main方法
1.7. 配置
application.properties
1.8. 简化部署
把项目打成jar包,直接在服务器运行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
|
2 工程结构
2.1. 推荐工程结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| com
+- example
+- myproject
+- Application.java
|
+- domain
| +- Customer.java
| +- CustomerRepository.java
|
+- service
| +- CustomerService.java
|
+- web
| +- CustomerController.java
|
|
- root package:com.example.myproject,所有的类和其他package都在root package之下。
- 应用主类:Application.java,该类直接位于root package下。通常我们会在应用主类中做一些框架配置扫描等配置,我们放在root package下可以帮助程序减少手工配置来加载到我们希望被Spring加载的内容
- com.example.myproject.domain包:用于定义实体映射关系与数据访问相关的接口和实现
- com.example.myproject.service包:用于编写业务逻辑相关的接口与实现
- com.example.myproject.web:用于编写Web层相关的实现,比如:Spring MVC的Controller等
Spring Boot的应用主类会自动扫描root package以及所有子包下的所有类来进行初始化。
2.2. 非典型结构下的初始化
- 使用@ComponentScan注解指定具体的加载包
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| @SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan(basePackages="com.example")
public class Bootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Bootstrap.class, args);
}
}
|
- 使用@Bean注解来初始化。在主类中进行初始化。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @SpringBootApplication
public class Bootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Bootstrap.class, args);
}
@Bean
public CustomerController customerController() {
return new CustomerController();
}
}
|
3 两大特性——依赖管理
3.1. 依赖管理的原理
通过父项目进行依赖管理。通过starter进行依赖导入。
1
2
3
4
5
| <parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
|
mypom.xml
parent – spring-boot-starter-parent
parent – spring-boot-dependencies
几乎声明了所有的版本,查看Spring-boot-dependencies中的版本。可以自定义properties标签,修改版本号。
stater场景启动器。自动引入相关的所有依赖。可以自定义场景启动器,所有场景启动器最基本的以来。spring-boot-starter。引入依赖一部分可以不写版本号。引入非版本仲裁的版本号,必须要写。
修改默认的版本号,就近优先原则。
- 查看parent中定义了版本的key,在子项目中覆盖该key,即可修改该版本。
3.2. spring-boot-starter-web的依赖树
1
2
3
4
5
| cmd+B 声明和引用相互跳转
cmd+alt+B 实现和引用相互跳转
cmd+[/ cmd+] 前进后退
cmd+U 父项目
|
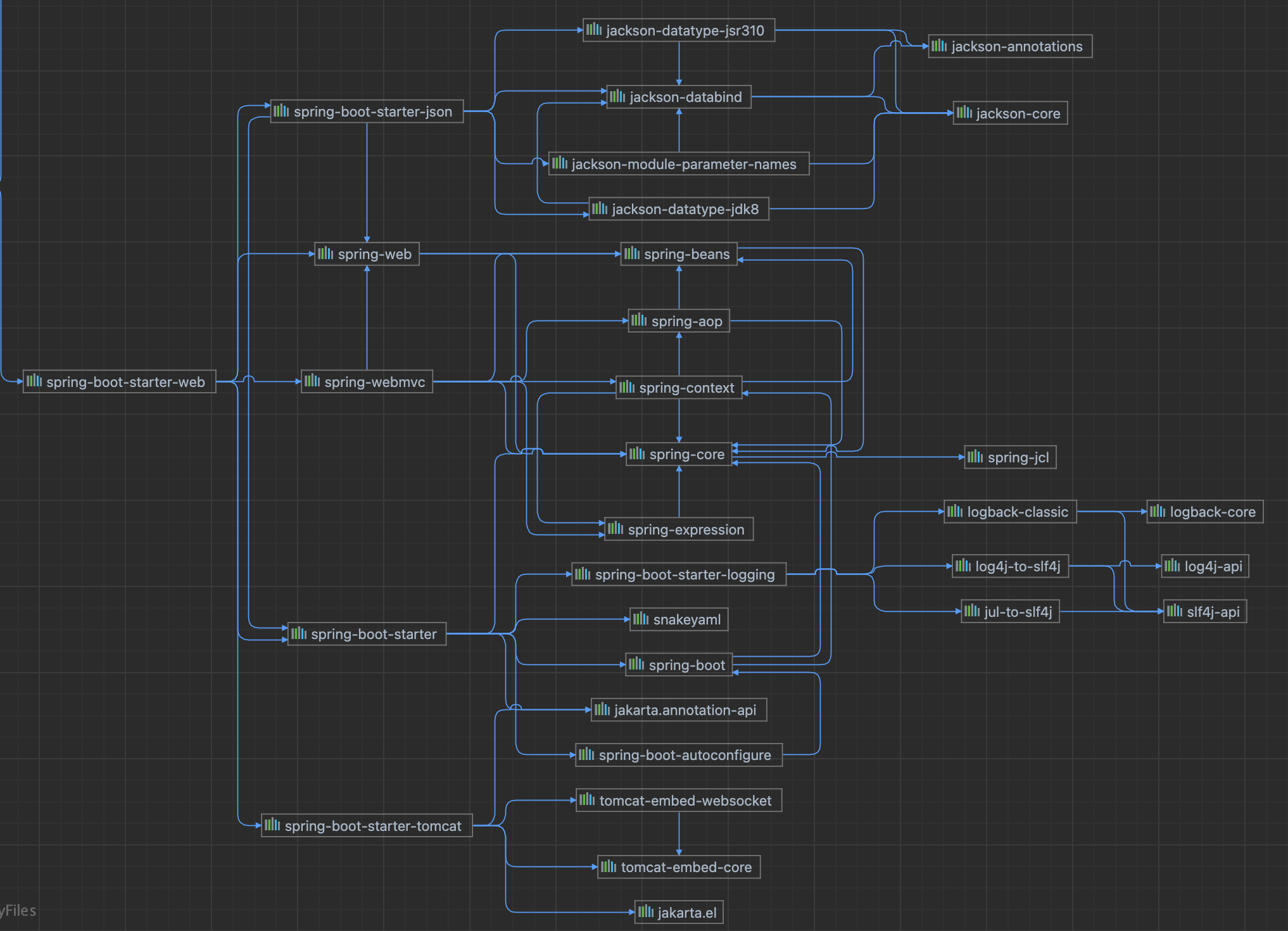
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| [INFO] \- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:jar:2.3.4.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter:jar:2.3.4.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot:jar:2.3.4.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-autoconfigure:jar:2.3.4.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-logging:jar:2.3.4.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | | +- ch.qos.logback:logback-classic:jar:1.2.3:compile
[INFO] | | | +- ch.qos.logback:logback-core:jar:1.2.3:compile
[INFO] | | | \- org.slf4j:slf4j-api:jar:1.7.30:compile
[INFO] | | +- org.apache.logging.log4j:log4j-to-slf4j:jar:2.13.3:compile
[INFO] | | | \- org.apache.logging.log4j:log4j-api:jar:2.13.3:compile
[INFO] | | \- org.slf4j:jul-to-slf4j:jar:1.7.30:compile
[INFO] | +- jakarta.annotation:jakarta.annotation-api:jar:1.3.5:compile
[INFO] | +- org.springframework:spring-core:jar:5.2.9.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | | \- org.springframework:spring-jcl:jar:5.2.9.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | \- org.yaml:snakeyaml:jar:1.26:compile
[INFO] +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-json:jar:2.3.4.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | +- com.fasterxml.jackson.core:jackson-databind:jar:2.11.2:compile
[INFO] | | +- com.fasterxml.jackson.core:jackson-annotations:jar:2.11.2:compile
[INFO] | | \- com.fasterxml.jackson.core:jackson-core:jar:2.11.2:compile
[INFO] | +- com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype:jackson-datatype-jdk8:jar:2.11.2:compile
[INFO] | +- com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype:jackson-datatype-jsr310:jar:2.11.2:compile
[INFO] | \- com.fasterxml.jackson.module:jackson-module-parameter-names:jar:2.11.2:compile
[INFO] +- org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-tomcat:jar:2.3.4.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | +- org.apache.tomcat.embed:tomcat-embed-core:jar:9.0.38:compile
[INFO] | +- org.glassfish:jakarta.el:jar:3.0.3:compile
[INFO] | \- org.apache.tomcat.embed:tomcat-embed-websocket:jar:9.0.38:compile
[INFO] +- org.springframework:spring-web:jar:5.2.9.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] | \- org.springframework:spring-beans:jar:5.2.9.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] \- org.springframework:spring-webmvc:jar:5.2.9.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] +- org.springframework:spring-aop:jar:5.2.9.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] +- org.springframework:spring-context:jar:5.2.9.RELEASE:compile
[INFO] \- org.springframework:spring-expression:jar:5.2.9.RELEASE:compile
|
4. 4 两大特性——自动配置
4.1. 自动配置的体现
- 自动配好了SpringMVC
- 引入了SpringMVC全套组件
- 自动配好了SpringMVC常用功能。字符编码问题、多文件上传问题
- 默认程序结构
- 主程序所在包及其所有子包里的文件和组件都能被扫描到。无需配置包扫描
- 可以修改SpringbootApplication注解参数中的扫描路径。或者ComponentScan注解。
- .properties中的文件是绑定到具体的Java类的。这些类会在容器中创建指定的对象。
- 按需加载所有的自动配置,自动配置都在spring-boot-autoconfigure包中
4.2. @ConfigurationProperties
@ConfigurationProperties是springboot提供读取配置文件的一个注解。
它是实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,在bean被实例化后,会调用后置处理,递归的查找属性,通过反射注入值,对大多数属性而言强制需提供其setter和getter方法。