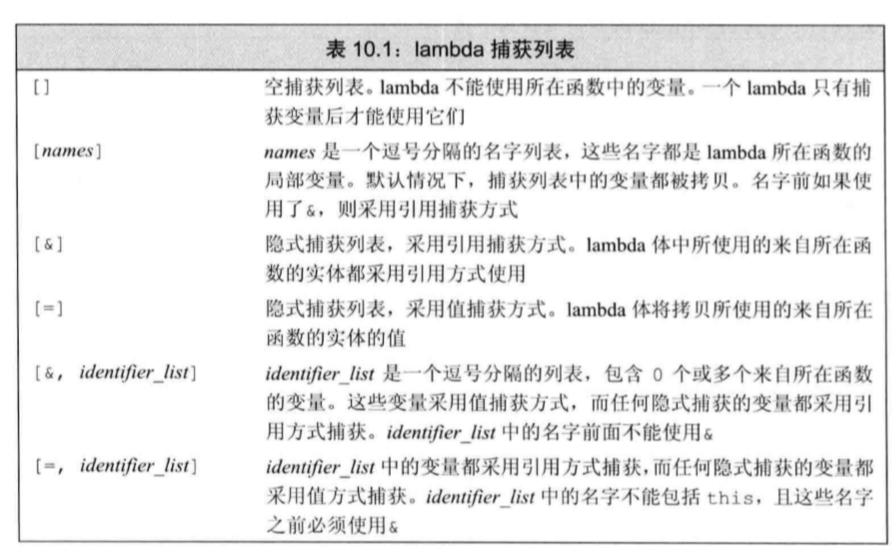
02 包装器类
0 概述
Number类
包装类(Integer、Long、Byte、Double、Float、Short)都是抽象类 Number 的子类
包装器类
Java为了能将8种基本类型当对象来处理,能够连接相关的方法,设置了包装器类。
- byte—Byte
- short—Short
- int — Integer
- long—Long
- char—Character
- float—Float
- double—Double
- boolean—Boolean
包装器类创建
由字面值或基本类型的变量创建包装器类对象的方法。
- 构造方法 new
1 | Integer i = new Interger(1); |
- 调用包装器类型的valueOf方法
1 | Double d = Double.valueOf(3.14); |
装箱拆箱
- 装箱Boxing: 将基本类型转化为包装器类型 包装器类.valueOf(基本数据类型变量或常量)。装箱共享内存。
- 拆箱unBoxing:将包装器类型转化为基本数据类型XX.XXXvalue();拆箱也共享内存
装箱操作
1 | Integer i = Integer.valueOf(10);//10是基本数据类型,i是包装器类型 |
拆箱操作
1 | Boolean.booleanValue() |
可以自动进行拆箱装箱
1 | Integer i = 4;//自动装箱。相当于Integer i = Integer.valueOf(4); |
注意事项
- 对象一旦赋值,其值不能在改变。
- ++/–自增自减运算符只能对基本数据类型操作
- 集合中只能存放包装器类型的对象
数据缓存池
new Integer(123) 与 Integer.valueOf(123) 的区别在于:
- new Integer(123) 每次都会新建一个对象;
- Integer.valueOf(123) 会使用缓存池中的对象,多次调用会取得同一个对象的引用。
1 | Integer x = new Integer(123); |
valueOf() 方法的实现比较简单,就是先判断值是否在缓存池中,如果在的话就直接返回缓存池的内容。
1 | public static Integer valueOf(int i) { |
在 Java 8 中,Integer 缓存池的大小默认为 -128~127。
1 | static final int low = -128; |
编译器会在自动装箱过程调用 valueOf() 方法,因此多个值相同且值在缓存池范围内的 Integer 实例使用自动装箱来创建,那么就会引用相同的对象。
1 | Integer m = 123; |
基本类型对应的缓冲池如下:
- boolean values true and false
- all byte values
- short values between -128 and 127
- int values between -128 and 127
- char in the range \u0000 to \u007F
在使用这些基本类型对应的包装类型时,如果该数值范围在缓冲池范围内,就可以直接使用缓冲池中的对象。
在 jdk 1.8 所有的数值类缓冲池中,Integer 的缓冲池 IntegerCache 很特殊,这个缓冲池的下界是 - 128,上界默认是 127,但是这个上界是可调的,在启动 jvm 的时候,通过 -XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=<size> 来指定这个缓冲池的大小,该选项在 JVM 初始化的时候会设定一个名为 java.lang.IntegerCache.high 系统属性,然后 IntegerCache 初始化的时候就会读取该系统属性来决定上界。
1 Character包装器
转义字符
\t在文中该处插入一个tab键\b在文中该处插入一个后退键\n在文中该处换行\r在文中该处插入回车\f在文中该处插入换页符\'在文中该处插入单引号\"在文中该处插入双引号\\在文中该处插入反斜杠
主要方法
- isLetter()
是否是一个字母 - isDigit()
是否是一个数字字符 - isWhitespace()
是否是一个空白字符 - isUpperCase()
是否是大写字母 - isLowerCase()
是否是小写字母 - toUpperCase()
指定字母的大写形式 - toLowerCase()
指定字母的小写形式 - toString()
返回字符的字符串形式,字符串的长度仅为1
2 Integer类
Integer类概述
包装一个对象中的原始类型 int 的值
Integer类构造方法及静态方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public Integer(int value) | 根据 int 值创建 Integer 对象(过时) |
| public Integer(String s) | 根据 String 值创建 Integer 对象(过时) |
| public static Integer valueOf(int i) | 返回表示指定的 int 值的 Integer 实例 |
| public static Integer valueOf(String s) | 返回保存指定String值的 Integer 对象 |
- 示例代码
1 | public class IntegerDemo { |
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来源 Estom的博客!