IOCBean管理基于XML方式 1 基于XMl方式创建对象 1 2 3 4 <bean id ="user" class ="com.ykl.User" > </bean > id:对象唯一标识 class:创建对象的类全路径,包类路径 name:对象名称标识
在Spring给你配置文件中,使用bean标签,标签里添加对应属性。实现对象的创建
bean中有很多属性
创建对象的时候,执行无参构造函数。
2 基于XML方式注入属性
DI依赖注入,就是注入属性。
原始的属性注入方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 package com.ykl;public class Book { private String name; public void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } public Book (String name) { this .name = name; } public Book () { } public static void main (String[] args) { Book book = new Book (); book.setName("123" ); Book book = new Book ("abc" ); } }
第一种方法:使用set方法进行注入.
创建属性和属性对应的set方法。
在Spring配置文件配置对象创建和属性注入。
加载配置文件获取指定的对象。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" > <bean id ="user" class ="com.ykl.User" > </bean > <bean id ="book" class ="com.ykl.Book" > <property name ="name" value ="shuming" > </property > </bean > </beans >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Test public void testBook () { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("bean01.xml" ); Book book = context.getBean("book" , Book.class); System.out.println(book.getName()); }
第二种方法:使用有参构造函数进行注入
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 package com.ykl;public class Order { private String oname; private String address; public Order (String oname, String address) { this .oname = oname; this .address = address; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <bean id ="order" class ="com.ykl.Order" > <constructor-arg name ="oname" value ="abc" > </constructor-arg > <constructor-arg name ="address" value ="China" > </constructor-arg > </bean > constructor-arg name 名称 value 值 index 参数列表
p名称空间注入方法
用于简化xml的配置方法。在beans里添加p命名空间
在bean标签里添加键值对。
1 2 3 4 <beans xmlns:p ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" > <bean id ="book" class ="com.ykl.Book" p:name ="shuming" > </bean >
xml注入其他类型的属性
1 2 3 <property name ="address" > <null /> </property >
1 2 <property name ="address" value ="<<南京>>" > </property >
1 2 3 4 5 <property name ="address" > <value > <![CDATA[<<南京>>]]> </value > </property >
级联Bean——外部bean注入
创建service和dao类
在配置文件中配置注入操作
测试类,测试是否注入成功
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public class UserService { public UserDao getUserDao () { return userDao; } public void setUserDao (UserDao userDao) { this .userDao = userDao; } UserDao userDao; public void add () { System.out.println("service add ..." ); userDao.update(); } } public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { @Override public void update () { System.out.println("dao update ..." ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" > <bean id ="userService" class ="com.ykl.service.UserService" > <property name ="userDao" ref ="userDao" > </property > </bean > <bean id ="userDao" class ="com.ykl.dao.UserDaoImpl" > </bean > </beans >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class Test02 { @Test public void testAdd () { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("bean02.xml" ); UserService user = context.getBean("userService" , UserService.class); user.add(); } }
级联Bean——内部bean
一对多关系:部门和员工。
在实体类之间表示一对多的关系。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 <bean id ="emp" class ="com.ykl.bean.Emp" > <property name ="ename" value ="lucy" > </property > <property name ="gender" value ="nv" > </property > <property name ="dept" > <bean id ="dept" class ="com.ykl.bean.Dept" > <property name ="dname" value ="security" > </property > </bean > </property > </bean >
数据库3BNF范式的要求:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 <bean id="emp" class="com.ykl.bean.Emp"> <!-- 普通属性 --> <property name="ename" value="lucy"></property> <property name="gender" value="nv"></property> <!-- 级联赋值-外部bean的方式 --> <property name="dept" ref="dept"> </property> <property name="dept.dname" value="jishubu"> </property> </bean> <bean id="dept" class="com.ykl.bean.Dept> <property name="dname" value="caiwubu"></property> </bean>
xml注入集合属性
注入数组类型属性、List集合类型属性、Map集合类型属性
创建集合类型的属性。
注入集合类型的属性
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 package com.ykl.collectiontype;import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.List;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Set;public class Student { private String[] courses; private List<String> list; private Map<String,String> maps; private Set<String> sets; public Student () { } public void setList (List<String> list) { this .list = list; } public void setMaps (Map<String, String> maps) { this .maps = maps; } public void setSets (Set<String> sets) { this .sets = sets; } public void setCourses (String[] courses) { this .courses = courses; } @Override public String toString () { return "Student{" + "courses=" + Arrays.toString(courses) + ", list=" + list + ", maps=" + maps + ", sets=" + sets + '}' ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 <bean id ="student" class ="com.ykl.collectiontype.Student" > <property name ="courses" > <array > <value > java</value > <value > c</value > </array > </property > <property name ="list" > <list > <value > zhangsan</value > <value > xiaosan</value > </list > </property > <property name ="maps" > <map > <entry key ="java" value ="java" > </entry > <entry key ="name" value ="hel" > </entry > </map > </property > <property name ="sets" > <set > <value > msyql</value > <value > redis</value > </set > </property > </bean >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 <bean > ...... <property name ="courseList" > <list > <ref bean ="course1" > </ref > <ref bean ="course2" > </ref > <ref bean ="course3" > </ref > </list > </property > </bean > <bean id ="course1" class ="com.ykl.collectiontype.Course" > <property name ="cname" value ="c1" > </property > </bean > <bean id ="course2" class ="com.ykl.collectiontype.Course" > <property name ="cname" value ="c2" > </property > </bean > <bean id ="course3" class ="com.ykl.collectiontype.Course" > <property name ="cname" value ="c3" > </property > </bean >
使用新的命名空间进行注入
在spring配置文件中引入util命名空间
提取list集合类型的属性注入。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:util ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd" > <util:list id ="bookList" > <value > zhangsan</value > <value > xiaosan</value > </util:list > <bean id ="book" class ="com.ykl.collectiontype.Book" > <property name ="bookList" ref ="bookList" > </property > </bean > </beans >
3 普通bean和工厂bean Spring中有两种类型的bean:
普通bean:在配置文件中定义的Bean类型就是返回类型
工厂bean:在配置文件中定义的Bean类型和返回类型可以不一样。
工厂bean的实现方法
创建类,让这个类作为工厂bean。实现接口factoryBean
实现接口里面的方法,在实现的方法中定义返回bean类型。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public class MyBean implements FactoryBean <Course> { @Override public Course getObject () throws Exception { Course course = new Course (); return course; } @Override public Class<?> getObjectType() { return null ; } @Override public boolean isSingleton () { return FactoryBean.super .isSingleton(); } } @Test public void testFactoryBean () { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("bean03.xml" ); Course myBean = context.getBean("mybean" , Course.class); System.out.println(myBean); }
1 <bean id ="mybean" class ="com.ykl.factorybean.MyBean" > </bean >
4 Bean的作用域
在Spring里可以设置Bean是单实例还是多实例。
在Spring里,默认情况下是,bean是单实例对象。
在spring文件bean标签里面的属性scope用于设置是单实例还是多实例。
scope=singleton,表示单实例对象。
scope=prototype,表示多实例对象。
1 2 <bean id ="book" class ="com.ykl.collectiontype.Book" scope ="prototype" > </bean >
singleton在加载配置文件的时候,就会创建单实例对象。饿汉式。
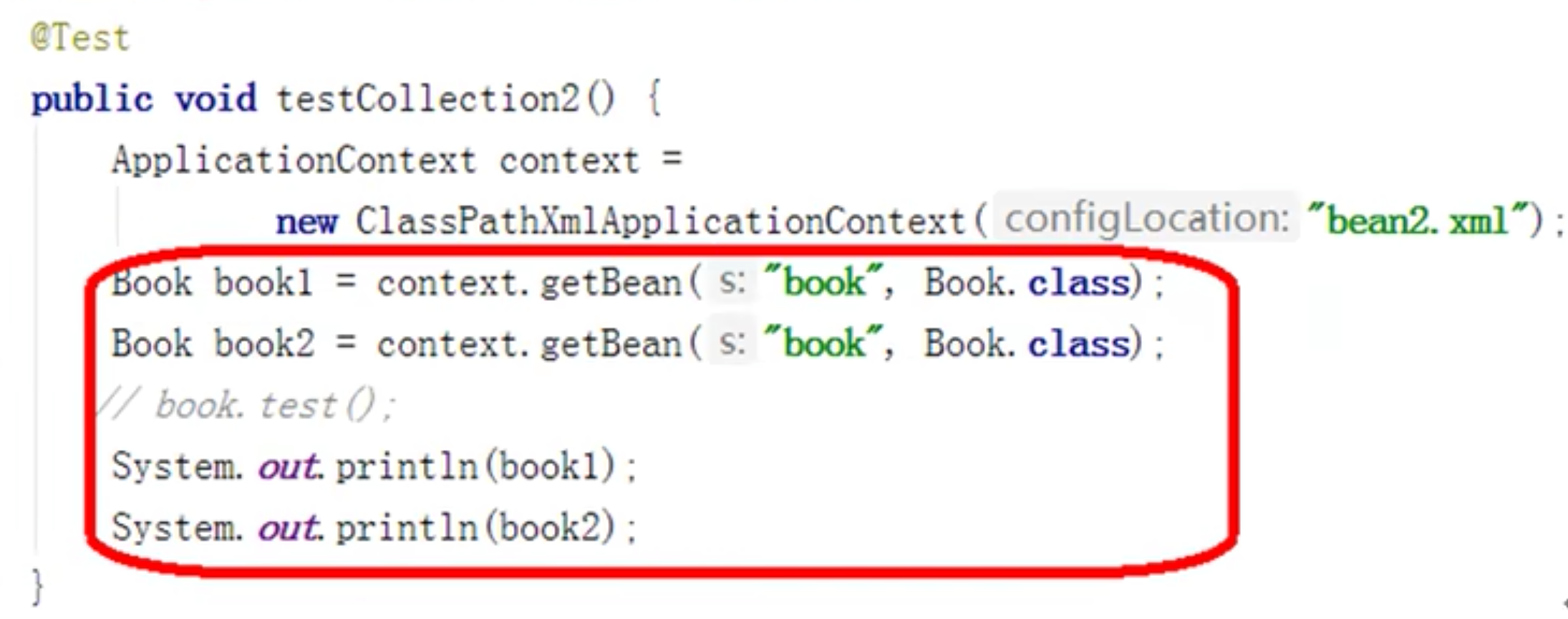
prototype在调用getBean方法的时候,才会创建对象。懒汉式。
这个跟之前记录的BeanFactory和ApplicationContext的区别有点像。不如就说BeanFactory默认scope为prototype,ApplicationContext默认scope为singleton。
5 Bean的生命周期 基本步骤 从对象创建到对象销毁的过程。包括五个最基本的步骤。
通过构造器创建bean实例。
为bean的属性设置值和对其他bean的引用(调用set方法)
调用bean中初始化的方法(需要进行配置)
bean可以使用了
当容器关闭的时候,调用bean的销毁方法(需要进行配置)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public class Order { private String oname; public Order (String oname) { this .oname = oname; } public Order () { System.out.println("第一步 执行无参构造函数创建bean实例" ); } public void setOname (String oname) { this .oname = oname; System.out.println("第二步 调用set方法设置属性值" ); } public String getOname () { return oname; } public void initMethod () { System.out.println("第三部 调用初始化方法" ); } public void destroyMethod () { System.out.println("第五步 调用销毁方法" ); } } @Test public void testCollection () { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ("bean05.xml" ); Order order = context.getBean("order" , Order.class); System.out.println("第四步 获取bean实例对象" ); ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)context).close(); }
1 2 3 <bean id ="order" class ="com.ykl.bean.Order" scope ="singleton" init-method ="initMethod" destroy-method ="destroyMethod" > <property name ="oname" value ="hello world" > </property > </bean >
Post处理器步骤 添加后置处理器后,总共有7步
通过构造器创建bean实例。
为bean的属性设置值和对其他bean的引用(调用set方法)
把bean实例传递bean后置处理器的方法
调用bean中初始化的方法(需要进行配置)
把bean实例传递Bean后置处理器的方法
bean可以使用了
当容器关闭的时候,调用bean的销毁方法(需要进行配置)
实例:后置处理器的效果演示
创建类,实现接口BeanPostProcessor,创建后置处理器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class MyBeanPost implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("后置处理器,前置任务" );; return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("后置处理器,后置任务" ); return bean; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 <bean id ="order" class ="com.ykl.bean.Order" scope ="singleton" init-method ="initMethod" destroy-method ="destroyMethod" > <property name ="oname" value ="hello world" > </property > </bean > <bean id ="mybeanpost" class ="com.ykl.bean.MyBeanPost" > </bean >
6 自动装配
手动装配:通过property的那么和value属性。
自动装配:根据指定装配规则(属性名称或者属性类型),Spring自动将匹配的属性值进行注入。
bean标签autowire实现自动装配。autowire通常包含连个值
byName根据属性名称注入(bean的id和属性名称一致)
byType根据属性类型注入(如果该类型有多个实例会出错)
1 2 3 4 <bean id ="emp" class ="com.ykl.autowire.Emp" autowire ="byName" > </bean > <bean id ="dept" class ="com.ykl.autowire.Dept" > <property name ="dname" value ="hello" > </property > </bean >
7 外部属性文件 直接配置数据信息 1 2 3 4 5 6 <bean id ="dataSource" class ="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" > </property > <property name ="url" value ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user" > </property > <property name ="username" value ="root" > </property > <property name ="password" value ="123456" > </property > </bean >
引入外部属性文件配置数据库连接池
编辑外部属性文件.properties
引入外部属性文件,添加新的命名空间context
1 2 3 4 prop.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver prop.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user prop.username=root prop.password=123456
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:util ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd" > <bean id ="dataSource" class ="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" > </property > <property name ="url" value ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user" > </property > <property name ="username" value ="root" > </property > <property name ="password" value ="123456" > </property > </bean > <context:property-path path ="classpath:jdbc.properties" /> <bean id ="dataSource" class ="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" > <property name ="driverClassName" value ="${prop.driverClass}" > </property > <property name ="url" value ="${prop.url}" > </property > <property name ="username" value ="${prop.username}" > </property > <property name ="password" value ="${prop.password}" > </property > </bean > </beans >