网络操作
https://blog.csdn.net/forezp/article/details/88414741
1 网络编程基础
Java 中的网络支持:
- InetAddress:用于表示网络上的硬件资源,即 IP 地址;
- URL:统一资源定位符;
- Sockets:使用 TCP 协议实现网络通信;
- Datagram:使用 UDP 协议实现网络通信。
InetAddress
没有公有的构造函数,只能通过静态方法来创建实例。
1
2
| InetAddress.getByName(String host);
InetAddress.getByAddress(byte[] address);
|
URL
可以直接从 URL 中读取字节流数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
URL url = new URL("http://www.baidu.com");
InputStream is = url.openStream();
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is, "utf-8");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}
|
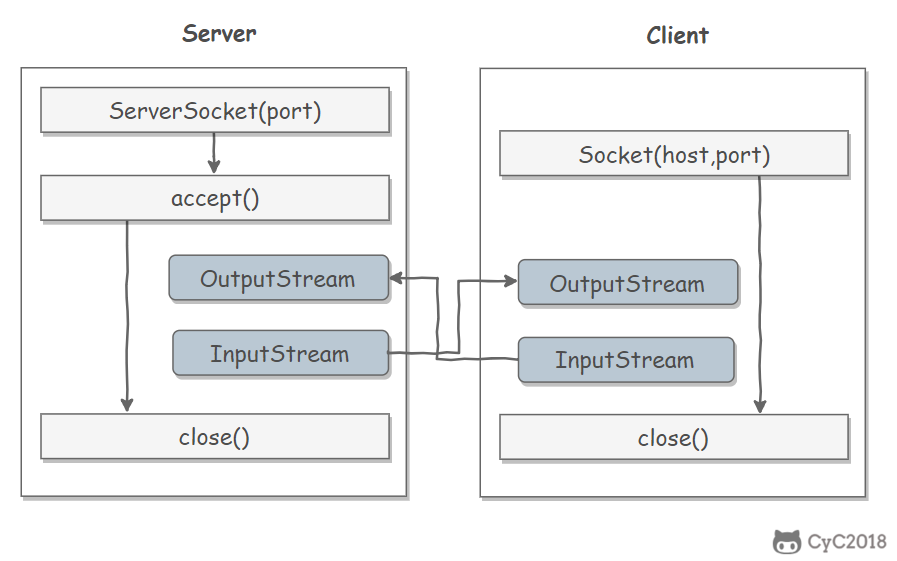
Sockets
- ServerSocket:服务器端类
- Socket:客户端类
- 服务器和客户端通过 InputStream 和 OutputStream 进行输入输出。
Datagram
- DatagramSocket:通信类
- DatagramPacket:数据包类
2 BIO Socket编程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| public class PlainOioServer {
public void serve(int port) throws IOException {
final ServerSocket socket = new ServerSocket(port);
try {
for (;;) {
final Socket clientSocket = socket.accept();
System.out.println("Accepted connection from " + clientSocket);
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
OutputStream out;
try {
out = clientSocket.getOutputStream();
out.write("Hi!\r\n".getBytes(Charset.forName("UTF-8")));
out.flush();
clientSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
try {
clientSocket.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
}
}
}
}).start();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
3 NIO Socket编程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
| public class NIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssChannel.configureBlocking(false);
ssChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
ServerSocket serverSocket = ssChannel.socket();
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8888);
serverSocket.bind(address);
while (true) {
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = keys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel1 = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel1.accept();
sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
sChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel sChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
System.out.println(readDataFromSocketChannel(sChannel));
sChannel.close();
}
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
}
private static String readDataFromSocketChannel(SocketChannel sChannel) throws IOException {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
StringBuilder data = new StringBuilder();
while (true) {
buffer.clear();
int n = sChannel.read(buffer);
if (n == -1) {
break;
}
buffer.flip();
int limit = buffer.limit();
char[] dst = new char[limit];
for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++) {
dst[i] = (char) buffer.get(i);
}
data.append(dst);
buffer.clear();
}
return data.toString();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);
OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream();
String s = "hello world";
out.write(s.getBytes());
out.close();
}
}
|