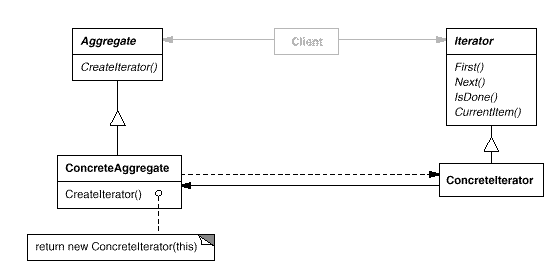
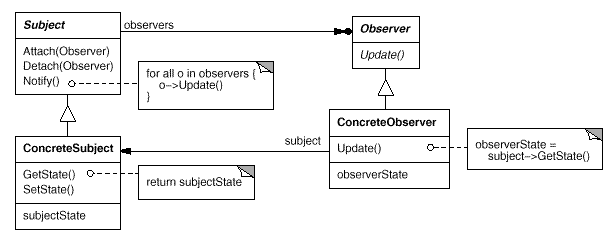
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>组件通信-父子通信案例(watch实现)</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<cpn :number1='num1' :number2='num2' @num1change="num1Change" @num2change="num2Change"></cpn>
<h2>父组件{{num1}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="num1" >
<h2>父组件{{num2}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="num2">
</div>
<template id="cpn">
<div>
<h2>{{number1}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="dnumber1">
<h2>{{number2}}</h2>
<input type="text" v-model="dnumber2">
</div>
</template>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const cpn = {
template: "#cpn",
data() {
return {
dnumber1:this.number1,
dnumber2:this.number2
}
},
props:{
number1:[Number,String],
number2:[Number,String],
},
watch: {
dnumber1(newValue){
this.dnumber1 = newValue * 100
this.$emit('num1change',newValue)
},
dnumber2(newValue){
this.dnumber1 = newValue * 100
this.$emit('num2change',newValue)
}
},
};
const app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data() {
return {
num1:1,
num2:2,
}
},
methods: {
num1Change(value){
this.num1=value
},
num2Change(value){
this.num1=value
}
},
components: {
cpn
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
|