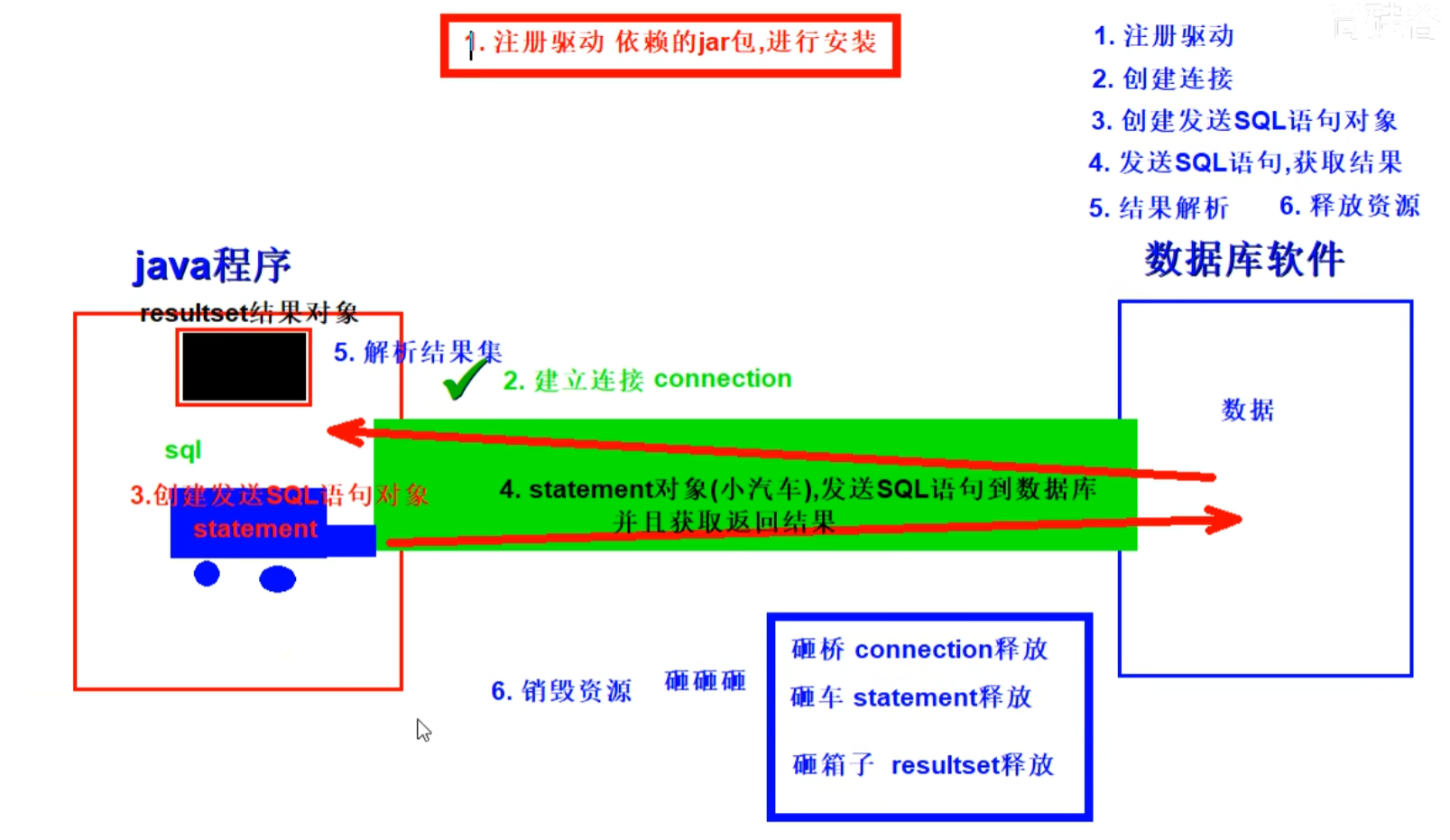
1 使用方法
批量执行SQL语句
批量执行 SQL 语句
当需要成批插入或者更新记录时,可以采用 Java 的 批量 更新 机制,这一机制允许多条语句一次性提交给数据库批量处理。通常情况下比单独提交处理更有效率
JDBC 的批量处理语句包括下面三个方法:
- addBatch(String):添加需要批量处理的 SQL 语句或是参数;
- executeBatch():执行批量处理语句;
- clearBatch(): 清空缓存的数据
通常我们会遇到两种批量执行 SQL 语句的情况:
- 多条 SQL 语句的批量处理;
- 一个 SQL 语句的批量传参;
使用实例
向数据表中插入20000条数据
实现层次一:使用 Statement
1
2
3
4
5
6
| Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
for(int i = 1;i <= 20000;i++){
String sql = "insert into goods(name) values('name_' + "+ i +")";
st.executeUpdate(sql);
}
|
实现层次二:使用 PreparedStatement
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into goods(name)values(?)";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i = 1;i <= 20000;i++){
ps.setString(1, "name_" + i);
ps.executeUpdate();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("花费的时间为:" + (end - start));
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps);
|
实现层次三
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
@Test
public void testInsert1() throws Exception{
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into goods(name)values(?)";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i = 1;i <= 1000000;i++){
ps.setString(1, "name_" + i);
ps.addBatch();
if(i % 500 == 0){
ps.executeBatch();
ps.clearBatch();
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("花费的时间为:" + (end - start));
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps);
}
|
实现层次四
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
@Test
public void testInsert2() throws Exception{
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql = "insert into goods(name)values(?)";
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i = 1;i <= 1000000;i++){
ps.setString(1, "name_" + i);
ps.addBatch();
if(i % 500 == 0){
ps.executeBatch();
ps.clearBatch();
}
}
conn.commit();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("花费的时间为:" + (end - start));
JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps);
}
|
其中的优化点
一个 SQL 语句的批量传参:
优化1:
使用 PreparedStatement 替代 Statement
优化2:
使用 addBatch() / executeBatch() / clearBatch()
?rewriteBatchedStatements=true&useServerPrepStmts=false
使用更新的 mysql 驱动:mysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jar
优化3:
Connection 的 setAutoCommit(false) / commit()